A centrifugal pump is a hydraulic machine that operates on a liquid using centrifugal force to convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. These are the most common types of bottom-up fluid transfer pumps. Used in agriculture, municipalities (water and wastewater treatment plants), industry, power plants, petroleum, mining, chemical, pharmacy, and many other industries.
Working Principle of Centrifugal Pump

A centrifugal pump relies on centrifugal force. The centrifugal pump consists of a fixed volume rotating impeller (cover). The liquid enters the impeller’s eye through the suction port. Speed of the rotating impeller causes the liquid to be released through the discharge nozzle.
The liquid enters the inlet of the centrifugal pump at atmospheric pressure and flows through the impeller. The rotating impeller’s centrifugal force exerted on the fluid causes the fluid to move through the impeller eye and along the impeller blades towards its end. The liquid is then pressed into the inner wall and discharged through the pump drain opening. Due to the pressure drop in the suction pump and impeller eye, the liquid is drawn into the pump by passing a steady stream through the pump.
Types of centrifugal pumps
The centrifugal pump has the following types:
1) Axial flow pump
- Pushes the liquid impeller parallel to the pump axis.
- More pressure is created when advancing or raising the blade on liquid.
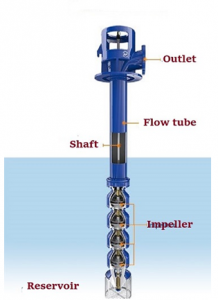
2) Submersible pump
A submersible pump, also known as an electric submersible pump, is a pump that fully submerges in the fluid. The motor’s body of this pump is sealed and tightly fixed.
They transfer water by transferring rotational energy from mobile energy to surface pressure. This is done by injecting water into the pump: first, it forces the water from impeller into the diffuser and then transfer it.
The bi advantage of a submersible pump is that it doesn’t require to refill because it is fully immerged in liquid. They don’t require a lot of energy to transfer water to the pump.
3) Jet Pumps
The jet pump is installed above the ground and cannot be submerged. They are generally used to pump water from wells through suction pipes to provide drinking water or pressurized sanitary water. Other common (but limited) applications are commercial and light irrigation and water supply for irrigation systems. Jet pumps are generally more popular in areas with hot climates or high groundwater levels.
It is important to note that the jet pump must not dry out. Operating the pump in standby mode can seriously and permanently damage it.
These pumps must be started before preparing to collect water. To start the jet pump, first, make sure the pump power is turned off. Then, remove the oil filler cap on the wet end of the pump (or in front of the engine). Then fill the water inlet with water so that the water reaches the top of the drain. The idea behind it is to let all the air out of the pump casing. Participate in the KBC Online Game and change your lifestyle today.
Advantages and disadvantages of a centrifugal pump
Centrifugal pumps are the most popular type of pumps for feeding liquids. Centrifugal pumps have many advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of Centrifugal Pumps
- A centrifugal pump is easy to use.
- It needs low maintenance and initial cost.
- They generate excessive pressure is created in the chamber.
- The impeller and the shaft are the only moving parts.
- These types of pumps have quiet performance.
- Wide range of pressures, flow rates, and flow rates.
- Use smaller footprints in different places.
Disadvantages of Centrifugal Pumps
- It does not use liquids correctly.
- Compared to other types of pumps (e.g., stationary turbines), centrifugal pumps are generally not able to use high-pressure programs.
- Under normal circumstances, centrifugal pumps cannot create high pressure without changing the design and are not suitable for providing high pressure with low flow, with the exception of multistage pumps.
Application of the centrifugal pump
- Oil and crude oil, sludge, waste from sewage pumps; Used in oil refineries and power plants
- Industrial industries in the fast and fire industry: heating and ventilation, boiler water application, air conditioning, pressure, fire system.
- Waste Management, Agricultural and Wastewater Treatment Plant, Urban Cities, Flow, Natural Gas Treatment, Irrigation, and Flood Control.
- Pharmaceutical and chemical.